May 6th, 2025
The U.S. financial markets are the cornerstone of global trading, offering unmatched liquidity, scale, and growth potential. For APAC-based firms, these markets represent an opportunity to expand into the world’s largest financial ecosystem. However, their complexity- characterized by fragmented liquidity, diverse participants, and stringent regulations- requires a strategic approach.
This guide offers a comprehensive introduction to the U.S. equities and options markets, highlighting their unique features and challenges to help APAC firms prepare for a successful entry.
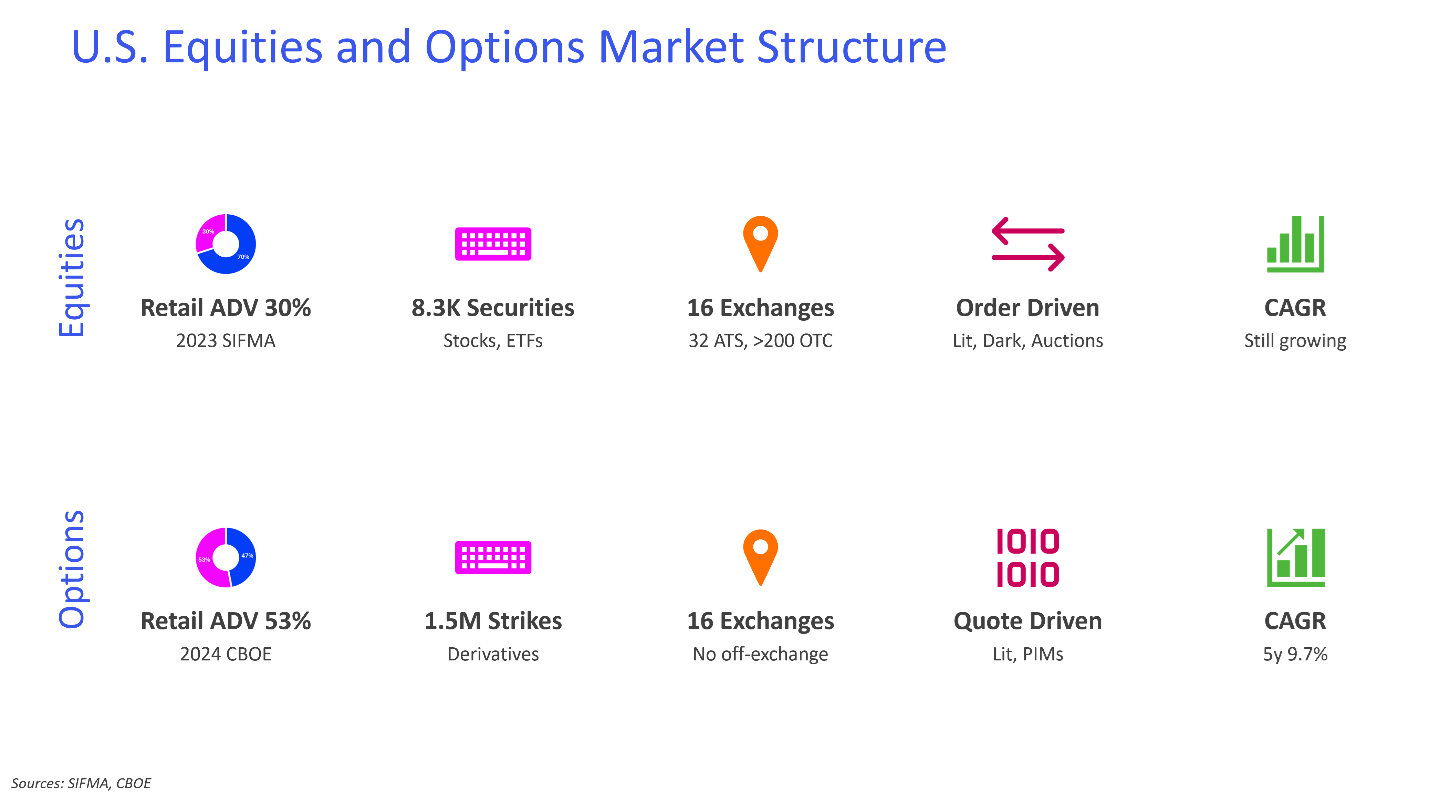
The Size and Scope of the U.S. Markets
U.S. Equities Market
The U.S. equities market is the largest and most liquid in the world, hosting an extensive array of publicly traded companies across industries. Major exchanges such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and NASDAQ are global financial hubs, facilitating billions of shares traded daily. This activity spans 16 lit exchanges, with an additional significant portion- up to 50% of daily trading volume- occurring in dark pools. These off-exchange venues provide institutional investors with the means to execute large trades discreetly, ensuring minimal market disruption.
Retail participation has surged, transforming the equities landscape. Since the pandemic, retail investors have driven daily trading volume to approximately 30%, up from just 10% a few years ago. Commission-free platforms and mobile-friendly apps have democratized access to equities trading, allowing millions to engage in markets once dominated by institutions. This growing retail activity presents unique opportunities for APAC firms to tap into robust liquidity while addressing the needs of a dynamic investor base.
U.S. Options Market
The U.S. options market is also large and liquid, offering investors a wide range of strategies, from simple call and put options to complex spreads. With record-breaking trading volumes, the market has become a cornerstone for both retail and institutional investors. A popular trend is the rise of zero-days-to-expiration (0DTE) options, contracts that expire the same day they are traded. While these instruments offer high-risk, high-reward opportunities, they also demand sophisticated risk management.
Unlike equities, options trading is confined to 16 lit exchanges with no dark pools. Market makers play a pivotal role, providing liquidity for the vast number of option strikes and expirations. This structure ensures consistent market activity but requires advanced systems for order routing and margin management. For APAC firms, the options market represents a gateway to substantial growth, provided they can navigate its complexity and meet U.S. regulatory standards.
Key Features of the U.S. Market Structure
The U.S. markets are distinct in their structure, presenting both opportunities and challenges. Fragmented liquidity is a hallmark feature, with trading dispersed across multiple exchanges. In equities, this fragmentation is compounded by dark pools, which handle a significant portion of volume but operate under strict regulatory oversight. For options, all trading occurs on lit exchanges, where market makers ensure liquidity for a vast array of contracts.
Regulatory compliance is another critical aspect. Overseen by regulators such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) and the Options Clearing Corporation (OCC), the U.S. markets demand strict adherence to rules governing pre-trade, in-trade, and post-trade activities. Firms must manage complex requirements such as Reg T and portfolio margin calculations, ensuring both operational efficiency and investor protection.
The operational dynamics of equities and options further underscore their uniqueness. Equities trading is predominantly customer order-driven, with dark pools offering an added layer of anonymity for institutional transactions. Options, on the other hand, are quote-driven markets reliant on market-makers, whose role is to maintain liquidity across numerous strikes and expirations. These distinctions require tailored approaches to technology and strategy for effective participation.
The Rise of Retail Investors
Retail investors have reshaped the U.S. markets, particularly in equities and options. The pandemic acted as a catalyst, as millions turned to trading platforms offering commission-free access and intuitive user interfaces. Retail activity in equities has grown dramatically, with investors now accounting for nearly one-third of daily trading volume.
In options markets, retail participation has been equally transformative. Strategies like 0DTE options have gained popularity, allowing retail traders to speculate on intraday movements. While these opportunities attract significant interest, they also introduce risks that require robust systems for risk assessment and margin management.
For APAC firms, this trend is both a challenge and an opportunity. Meeting the demands of retail investors requires platforms that combine ease of use with advanced functionality. Firms must also implement systems to mitigate risks, ensuring retail clients are protected from overexposure, particularly in volatile market conditions.
Common Challenges for Foreign Firms Entering the U.S. Market
Entering the U.S. markets requires overcoming a series of unique challenges. Navigating fragmented liquidity is one of the most pressing issues, as firms must route orders efficiently across multiple venues to ensure best execution. In equities, dark pools add an extra layer of complexity, while options markets demand seamless connectivity to lit exchanges.
Regulatory compliance is another significant hurdle. The U.S. markets are heavily regulated, with strict requirements for risk and margin management. Firms must adhere to rules governing pre-trade validation, real-time risk monitoring, and post-trade reporting. The consequences of non-compliance can be severe, including financial penalties and reputational damage.
Technology infrastructure also poses challenges. The U.S. markets demand scalable systems capable of handling high trade volumes and complex margin calculations. For foreign firms, building or adapting technology to meet these demands can be resource-intensive. However, partnering with a trusted technology provider can simplify this process, enabling firms to focus on growth.
Charting a Path to Success in the U.S. Markets
Successfully entering the U.S. markets requires strategic preparation and the right technology. For APAC firms, navigating fragmented liquidity, regulatory compliance, and real-time risk management are pressing challenges. Leveraging effective tools can help APAC firms streamline complexities and enable more efficient resource allocation.
Equally important is educating both teams and clients. Internal staff must understand the nuances of U.S. market structure, while clients- particularly retail investors- benefit from clear guidance on trading strategies and risk management. A balanced approach that combines advanced tools with focused education can help firms build a strong foundation for long-term success.
In the next blog post, we’ll explore the unique complexities of the U.S. options market and how partnering with Sterling can ensure a successful market entry for APAC -based firms. Let us guide your market entry strategy- contact us today to learn more link.
We look forward to learning more about your trading needs.

Modernizing Margin | Why FINRA is Rethinking Margin Rules
This post is the first in a three-part series examining FINRA’s proposed intraday margin ...
Market Asymmetry Before It Moves You
In today’s markets, sharp price moves rarely come out of nowhere. They build quietly ...

Sterling OMS 360: A New Era in OMS
The newly launched OMS provides the only real-time margin and multi-asset capability during ...

The Intersection of Pre- and Post-Trade Risk
Effective risk management is paramount in today's fast-evolving financial landscape. Firms ...